S/M-21
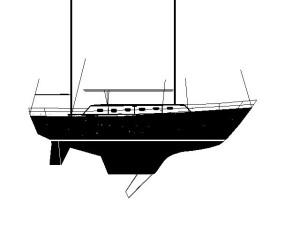
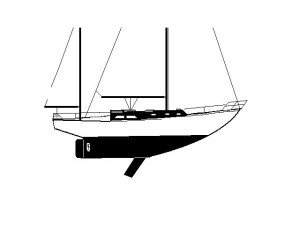
Hinckley Sou'wester 51 Yawl
51' x 24 Tons, Full Keel & CB
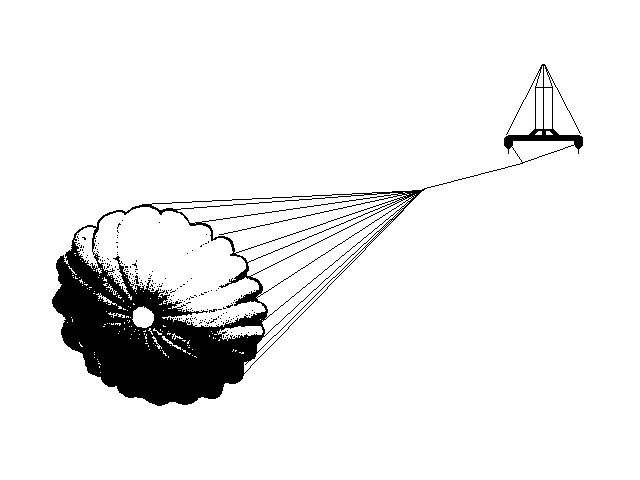
24-Ft. Dia. Sea Anchor
Force 9 Conditions
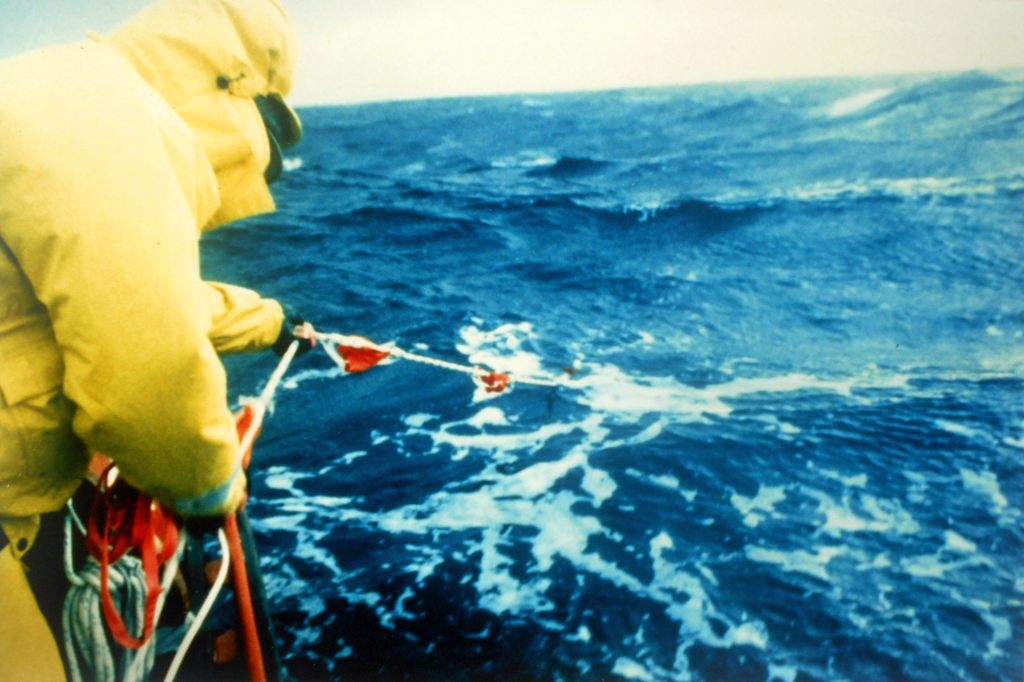
File S/M-21, obtained from Captain Eric F. Roos, Mt. Desert, ME. - Vessel name Windcrest, hailing port Bar Harbor, Hinckley Sou'wester yawl, designed by McCurdy and Rhodes, LOA 51' x LWL 37' 6" x Beam 14' x Draft 6' (11' with CB down) x 24 Tons - Full keel & auxiliary centerboard - Sea anchor: 24-ft. diameter Para-Tech on 400' x 3/4" nylon braid and 100' of 5/16" chain with 3/4" stainless steel swivel - Deployed in deep water about 120 miles south of Nantucket Island in a whole gale with winds of 40-50 knots and seas of 20 feet - Vessel's bow yawed 15° - Drift was 14 n.m. during 23 hours at sea anchor.
Windcrest was en route to Bermuda from Bar Harbor when she ran into bad weather. Transcript of feedback obtained from Captain Eric F. Roos:
Para-Anchor was deployed due to deteriorating weather conditions close to the North wall of the Gulf Stream. Our weather forecast indicated that if we continued on our present course a large frontal system would pass over us just as we entered the Gulf Stream. We chose to sail away from the building seas near the stream and set our para-anchor while conditions were still tolerable and we still had daylight.
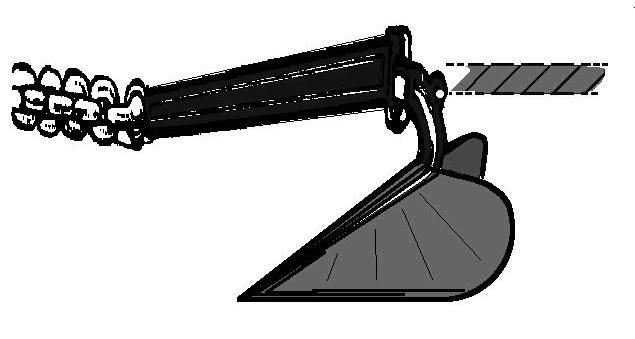
There was no sudden wind change, but rather a consistent increase in wind speed and building seas (max 50 knots with max 25-30' seas.) Since we deployed our para-anchor before conditions were too bad, the deployment was fairly straightforward. We chose to attach the shackle of the rode directly to our 60# plow anchor's welded cross-bar (v). After seizing the shackles we let out the 400' rode, anchor and 100' of 5/16" chain over the stainless steel bow roller. The weight of the anchor and chain provided an excellent catenary to absorb the shocks we experienced during the worst conditions. Our biggest concern the whole time we sat on the para-anchor was the strength of the cross-bar on the plow anchor. Though it held just fine, I wonder if I should have used a different attachment point.
Windcrest performed very well while on the sea anchor. She yawed from side to side a total of 30° [total arc]. At one point the anchor chain jumped out of the stainless steel roller (we forgot to put pin through top of roller) and found its way down the starboard side and into the stainless steel chock causing only cosmetic damage. Due to the rugged nature of our chocks, we would intentionally place the chain in the chock in the future.
After 23 hours the seas subsided to 15-20' and the winds moderated to less than 25 knots and began coming from a different direction than the seas. At this point Windcrest insisted on pointing into the wind rather than the seas. This caused considerable rolling and was the ultimate reason we retrieved the para-anchor when we did. The smashing/crashing sounds below were enough to make a man go mad. The retrieval was straightforward but more difficult than the deployment. We felt it was next to impossible to retrieve the tackle in an orderly fashion. We ended up with a heaping mess of rode and para-anchor lines. However, when we repacked the gear at a later date it was not as bad as we had anticipated. In summary, I have nothing but good things to say about the para-anchor equipment and would not go offshore without one.
(CAUTION: The steel anchor should be taken off in storms lest a breaking wave smash it against the boat.)
CAUTION: A big, heavy steel anchor may provide added catenary shock absorption hanging on the rode, but in a Fastnet type storm it may also get turned into a lethal object if it gets smashed against the boat by a breaking wave. It should be taken off, and the rode attached the chain itself.
Love the Drag Device Database? Help us to keep it free for all mariners by making a tiny donation to cover our server and maintenance costs. Thank You!