D/M-3
Monohull, Custom Ketch
50 x 22 Tons, Full Keel & Centerboard
36" Dia. Galerider
Force 10 Conditions
File D/M-3, obtained from Frank Snyder, Vice Commodore, New York Yacht Club - Vessel name Southerly, hailing port New York, monohull, center-cockpit aluminum ketch designed by Sparkman & Stephens, LOA 50' x LWL 45' x Beam 14' x Draft 5.5' x 22 Tons - Full keel & centerboard - Drogue: Galerider on 200' x 1¼" nylon three strand rode, with 1/2" stainless steel swivel - Deployed in low system in deep water in the Gulf Stream, with winds of 50 knots and seas of 10 ft. - Vessel's stern yawed 20° with helmsman steering - Speed was reduced to 3-4 knots.
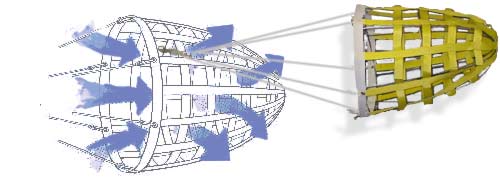
Frank V. Snyder, Vice Commodore of the New York Yacht Club, ran across an article in a British magazine summarizing the results of experiments conducted by the National Maritime Institute on life rafts in heavy weather, in the North Sea. The article emphasized the importance of sea anchors - small, synthetic cones - when it came to keeping life rafts from capsizing, but revealed that the same cones were often among the first parts of the raft to fail. The article went on to say that the Institute had then designed and built new sea anchors from a close mesh netting material which, unlike their predecessors, did not fail in a second set of sea trials. One raft even lost its ballast bags but still did not flip: its sea anchor held it down.
When preparing his 55-ft. ketch Southerly for a late fall passage from New York to Antigua in 1984, Commodore Snyder decided to equip her with a flow-through drogue of his own design. He approached Skip Raymond of the sailmaking firm of Hathaway, Reiser & Raymond, Inc., with his ideas. Raymond then went to work, building a small model at first, and then the full scale prototype of the first Galerider drogue. It was three feet in diameter and four feet long, shaped a little like a basket made from two-inch nylon webbing. On Saturday, November 17, Southerly departed New York Harbor and broad-reached all Saturday and Sunday morning, making better than eight knots in seas that were building. On Sunday afternoon the barometer began dropping rapidly and, by the time she entered the Gulf Stream at dusk, the wind had piped up to southwest, Force 9-10. Soon she was in very confused conditions, with two big seas crossing at an angle of 90°.
In a related article appearing in the September 1986 issue of Yachting Magazine entitled Galerider Handles a Gale, Frank Snyder wrote that despite being a big, strong, stiff and seakindly boat, Southerly couldn't handle the turmoil. He directed the crew to douse the trysail and they began running before it under bare poles, trying to keep the new seas slightly on the starboard quarter. But as the confused seas continued to build Southerly became unmanageable, now and then her speed racing up to 12 knots or more on the face of a bigger wave. To have her surging at these speeds under bare poles was alarming. The vicious cross seas would catch her on the downslide and roll her rail down under. Her hull form would then cause her to broach in the trough - dangerous if the waves got any bigger. It was time to deploy the Galerider. The rode, 200 feet of 1¼" nylon three strand, was attached to the drogue and the bitter end given four turns around the coffee grinder on the after deck (Southerly is a center-cockpit boat). In went the drogue. When it took hold there was no shock at all; in fact the crew couldn't tell for sure the precise moment when the drogue did take hold, but were soon aware that the boat was slowing down. Commodore Snyder writes that the effect of slowing the boat in that big, confused seaway was magical:
At one moment the boat had been charging like a mad bull, with the helmsman struggling at the wheel; in the next, she was docile and under full control. The helmsman found that Southerly would still answer her helm - though slowly - and that she could steer through about 90°. Everyone relaxed, and the off-watch turned in, even though the motion wasn't all that comfortable, with the cross sea still rolling us 20° either side of vertical. But the boat was safe.
The seas continued to build for the next three hours and several big ones came aboard over the stern, though no green water reached the cockpit. Had the cockpit been aft, it would probably have filled a couple of times. At 0200, the wind veered to north and began dropping. By 0400 it was down to Force 7, and the storm was over - another of those six-hour Gulf Stream "local lows." (Yachting Magazine, September 1986, by permission).
Commodore Snyder's creation has caught on and many offshore yachts now carry a Galerider on board. The "flow-through" concept is rugged, simple, stable, and does not get turned inside out. The stainless steel wire hoop that keeps the Galerider's mouth open can be folded on itself, allowing for compact storage.
Love the Drag Device Database? Help us to keep it free for all mariners by making a tiny donation to cover our server and maintenance costs. Thank You!