Monohull, Ericson
25' x 3 Tons, Swing Keel
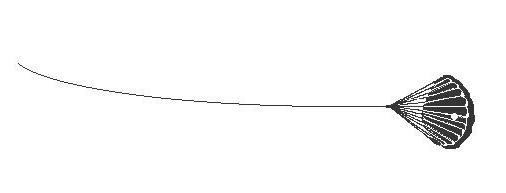
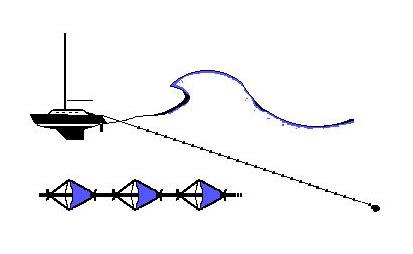
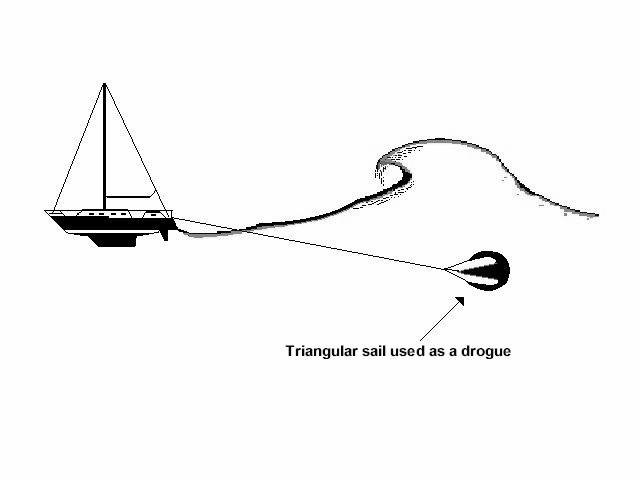
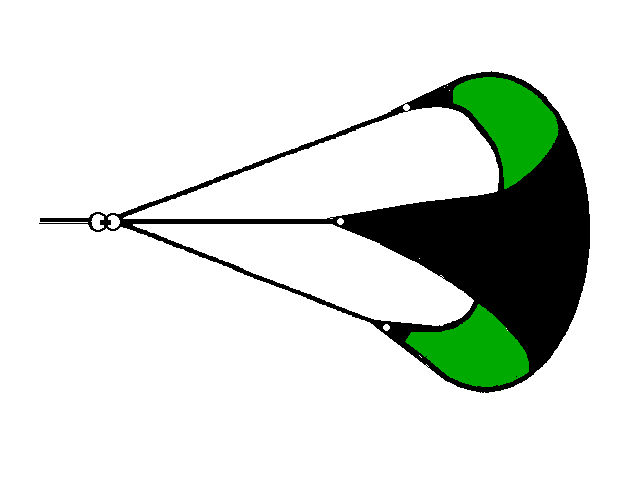
Jordan Series Drogue
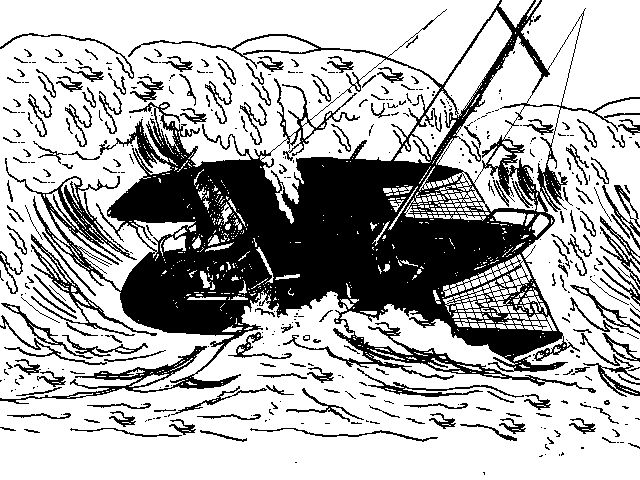
Force 8 Conditions
File D/M-6B, obtained from Gary Danielson, St. Clair Shores, MI. - Vessel name Moon Boots, hailing port Detroit, monohull, designed by Bruce King, LOA 24' 8" x LWL 20' 10" x Beam 8' x Draft 4' (27" keel up) x 3 Tons. Drogue: Galerider deployed in Force 8, mid-Atlantic - vessel required constant steering. Jordan series drogue (88 x 5" cones on 300' x 1/2" nylon braid rode) - Deployed in a gale in deep water about 500 miles east of the Bahamas with winds of 35-45 knots and seas of 9-14 ft. - Vessel's stern yawed 10° - Drift was about 10 miles during 36 hours of deployment.
This file updates the previous one. Gary Danielson's Lake Huron evaluations took place in 1988. In 1991 he sailed Moon Boots across the Atlantic and back. He had occasion to use the Galerider and the series drogue in a number of Force 8 gales. In the first mid-Atlantic gale he used the Galerider and found that it greatly enhanced steering control in 15-ft. seas, but left to itself (while he was resting down below) it would allow the stern of the boat to yaw too much - 40° off to each side at times. In the second Force 8 gale (600 miles from the British Isles and 15-ft. seas again) he used the series drogue and it kept the stern of the boat snubbed into the seas and, in taking total control of the situation, allowed him to remain down below and get much needed rest. Danielson sailed Moon Boots back across the Atlantic singlehanded in March 1991, re-tracing Columbus' route from the Canaries to San Salvador in the Bahamas. En route he ran into another Force 8 gale. Transcript:
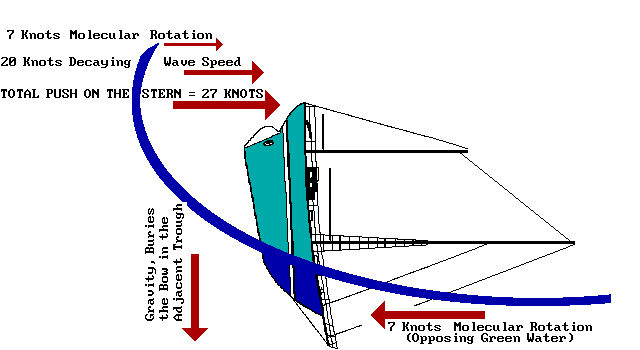
The only heavy weather of the trip occurred about 500 miles east of San Salvador, Bahamas. As my course was due West at that point, it meant the wind was right on the nose. At 25-30 knots Moon Boots can't sail upwind effectively any longer. Once the wind got to the low 30's I knew I'd have to put out a drogue. I decided to use the Jordan style series drogue rather than the Galerider because I didn't want to lose any of the ground I'd already gained and the Jordan is a much better "anchor" than the Galerider. In fact, that was pretty much how I decided which one to use on the prior trip also. In any event it did an outstanding job of keeping the stern into the waves and of limiting drift to almost nothing (10 miles in 36 hours, less any westerly drift from possible currents). I had changed the 15 lb. mushroom at the end to a 5 lb. weight and that helped the Jordan to ride a bit more horizontal (but still below the surface). The only problem was that the boat had been broken into in the Canaries and the inside lock for the main hatch had been damaged (the hatch fully closed, just couldn't be secured shut). As you probably know, the Jordan drogue exhibits a tremendous pull at all times. The transom of Moon Boots had been beefed up specially because of this, as had the hatch and the hatch boards. And a good thing too, because every so often a wave would completely go over Moon Boots (I could see solid water as I looked out the side ports).
The problem was that at times these waves would slide the main hatch 2-3' forward. Note that the hatch top itself was custom made of wood, weighted almost 75 lbs., and slid very hard on its track as it did not sit on rollers or cars of any type (just slid on metal tracks). It always took an effort with both hands to slide it open or shut. But these waves would slam it open and at the same time 30-50 gallons of water would pour in, (this happened 9 times in 36 hours). Therefore anyone using this style drogue had better have prepared the stern of his boat properly.
It has occurred to me that since the Jordan style drogue has a constant and continuous pull, it could make a superior sea anchor (off the bow) if sized properly for a given boat. It wouldn't work on Moon Boots as a sea anchor, but any boat that behaves OK with a sea anchor would probably be even safer with a Jordan style. I now believe, more than ever, that my solo Atlantic passages on Moon Boots could not have been accomplished safely without the drogues.
Love the Drag Device Database? Help us to keep it free for all mariners by making a tiny donation to cover our server and maintenance costs. Thank You!